
News: A Protein Found in Ticks Can Help Kill MRSA Infections
As researchers from Yale searched our environment for compounds to aid in the battle against drug-resistant bacteria, they got an unlikely assist from ticks.


As researchers from Yale searched our environment for compounds to aid in the battle against drug-resistant bacteria, they got an unlikely assist from ticks.
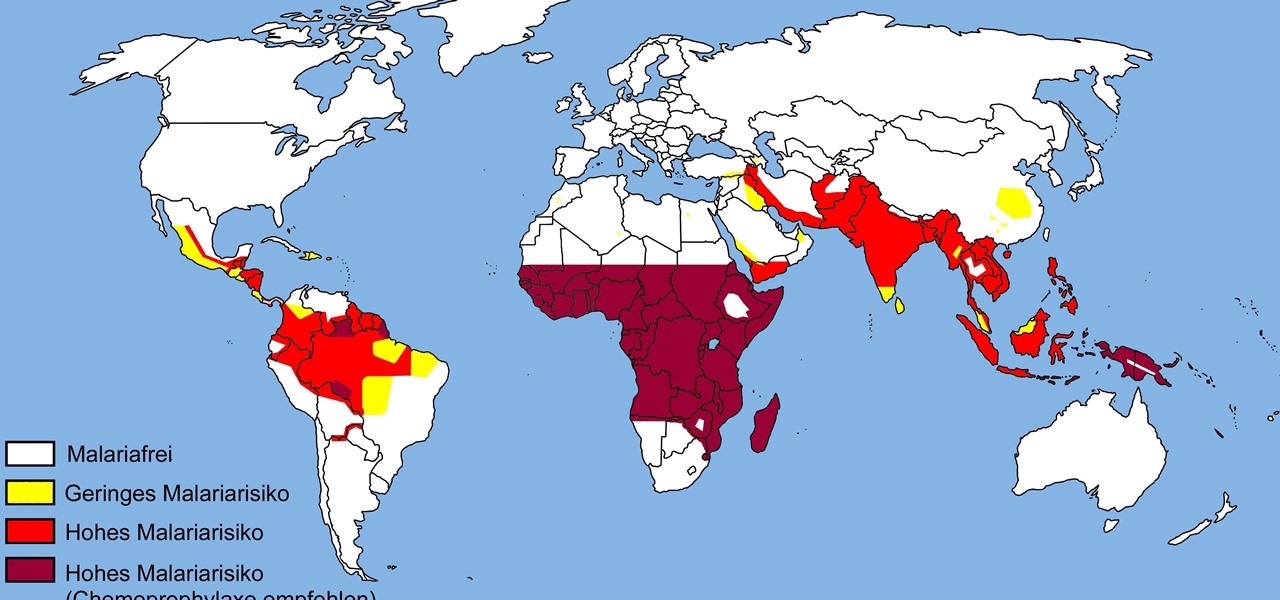
The theme for 2017's World Malaria Day, which is today, April 25, is "End Malaria for Good." For many Americans, this might seem like an odd plea. Especially since Malaria is seemingly an obsolete problem here. However, on World Malaria Day, it's important to remember the danger of malaria is still very much present in the US. And around the world, the disease is at the epicenter of a global crisis.

Hospitals are places we go to get well, and we don't expect to get sick or sicker there. But a study from researchers at the Cleveland Clinic, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, and Cleveland VA Medical Center in Ohio found that hospital floors in patient rooms were frequently contaminated with healthcare-associated pathogens—often dangerous multi-drug resistant bacteria.
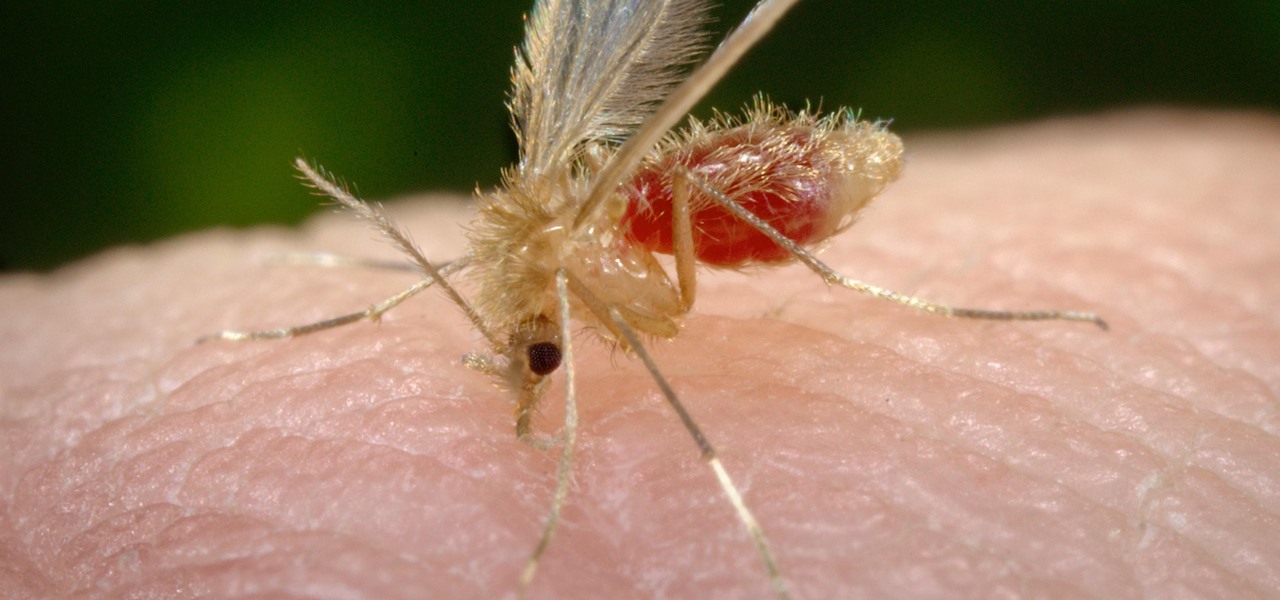

Transmitted by a sandfly one-third the size of a mosquito, parasitic Leishmania protozoa are responsible for a flesh-destroying disease that kills an estimated 20,000 people per year. Two new studies offer understanding of how the parasite provides immunity through persistence and why some people suffer more virulent forms of the disease.

As fun as it is to see Fido's face light up when you feed him table scraps, American dogs are getting fat. The good news is that research is homing in on nutritional strategies to boost canine capabilities to maintain a healthy weight.
Over 1.2 million people in the US are infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)—and one out of eight of them don't know it. Even after decades of intense research into the virus, there's still no cure for it. One of the big problems is that the virus hides out in certain cells of the body, resisting treatments that kill it.

Good day people, today we will examine some basic, for some people well-known attacks, also we will take a look at some advanced attacks.

Hey there, reader! In this tutorial we are going to explain how values are stored in variables as either signed or unsigned. Try to not get lost!

We all carry a bit of anxiety around with us. Is our boss still annoyed because we could barely stay awake in yesterday's pre-dawn meeting? Will our friend hate us forever because we forgot to call them back two weeks ago? Whatever worries pop up in your mind, whether they're monumental or insignificant, it can be hard to quiet those nagging voices, but you can shut down your nonstop mind with a bit of relaxation, distraction, and action.

By now, you've stuffed yourself with enough cranberry-soaked turkey to last you until next year. Still, there's a formidable amount of leftovers, and you're kidding yourself if you think you won't be craving them when you wake up tomorrow with a food coma/hangover.
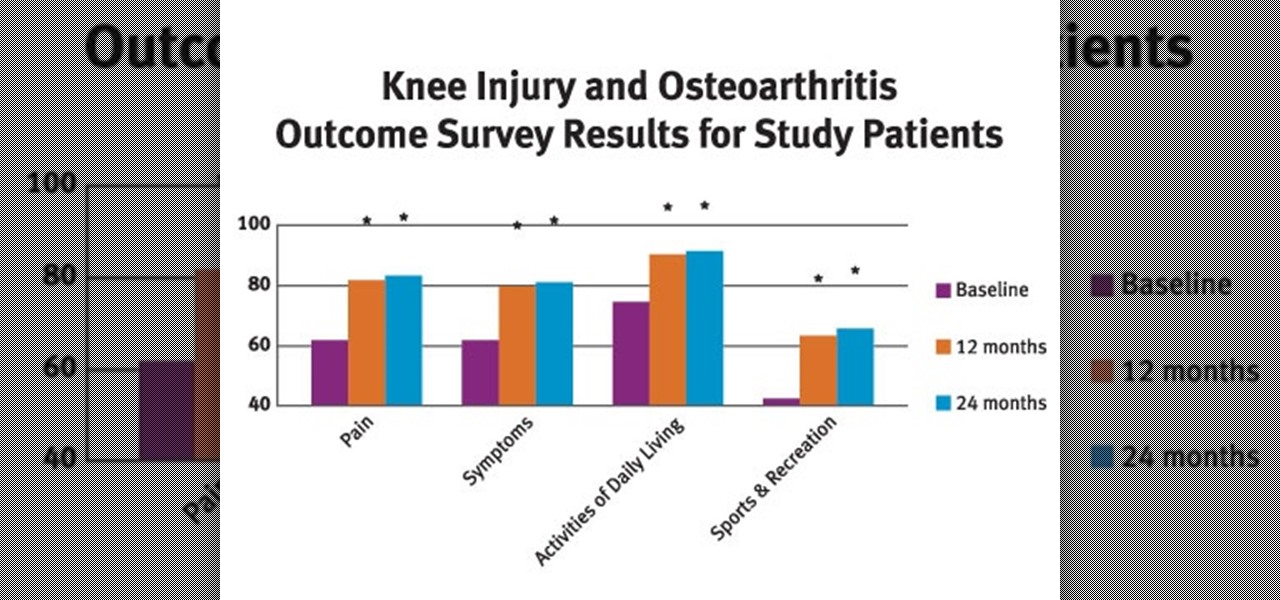
Osteoarthritis can affect every gender and at any age but it commonly occurs in women than in men. In America there are approximately 27 million Americans aged over 25 who live with osteoarthritis.
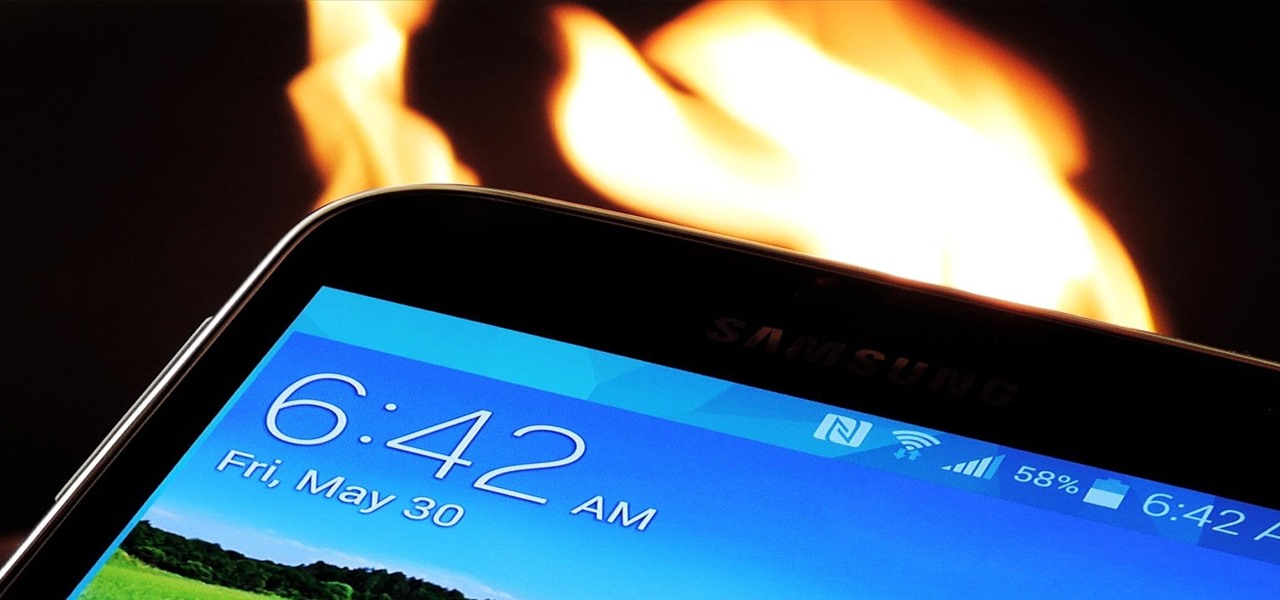

It's one hell of a device, but the Samsung Galaxy S5 is still susceptible to the many hazards that other smartphones are prone to: theft, cracked screens, poor battery life, and particularly, overheating.

Ever since the FBI took down the Silk Road and Dread Pirate Roberts last month, many questions have been raised about whether Tor still provides anonymity or not, and if it's now broken. I'll try to address that question here today succinctly from multiple angles, keeping it as simple and plain-language as possible. The Closing of Silk Road

Welcome back, my rookie hackers! When Wi-Fi was first developed and popularized in the late '90s, security was not a major concern. Unlike wired connections, anyone could simply connect to a Wi-Fi access point (AP) and steal bandwidth, or worse—sniff the traffic.

Perhaps the most important decoration of the holiday season is the Christmas tree. It's where all of the magic happens. If you're not into real Christmas trees, there's always some festive alternatives, but for those of us who can't live without a natural Christmas tree, choosing the right one for the right price can be an impossible task.

Microsoft Office files can be password-protected in order to prevent tampering and ensure data integrity. But password-protected documents from earlier versions of Office are susceptible to having their hashes extracted with a simple program called office2john. Those extracted hashes can then be cracked using John the Ripper and Hashcat.

While the iPhone XS and XS Max come equipped with 4 GB of random access memory, and the iPhone XR with 3 GB of RAM, Apple's latest flagships are still susceptible to occasional slowdowns in performance in iOS 12. This can be fixed by clearing RAM, but the process is now a little trickier compared to iPhones with Home buttons.
Unlike many browsers, Firefox gives a lot of control to the user. By default, Firefox does a great job of balancing security and performance. However, within the app's settings, you can modify options to shift this balance in one direction or another. For those looking to shift it toward security, here are few suggestions.
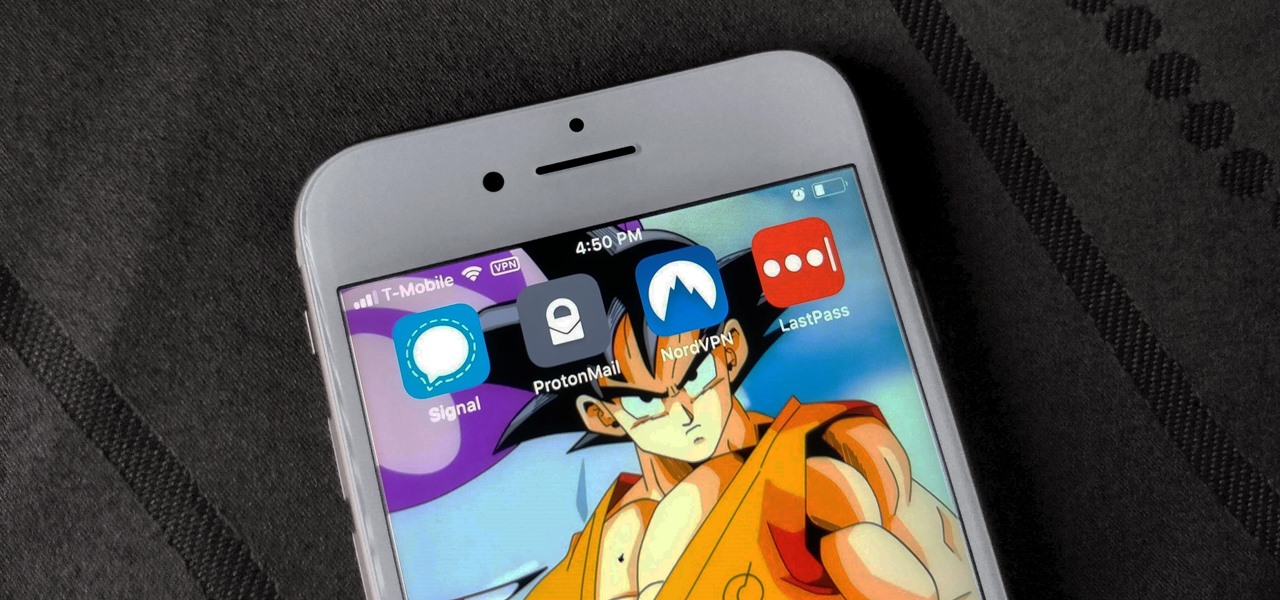
As the third-largest smartphone manufacturer in the world, Apple devices are a constant target for hackers everywhere. While iOS has seen fewer common vulnerabilities and exploits (CVEs) in recent years, iPhones still aren't hack-proof. Fortunately, you can strengthen your security with the help of a few apps.
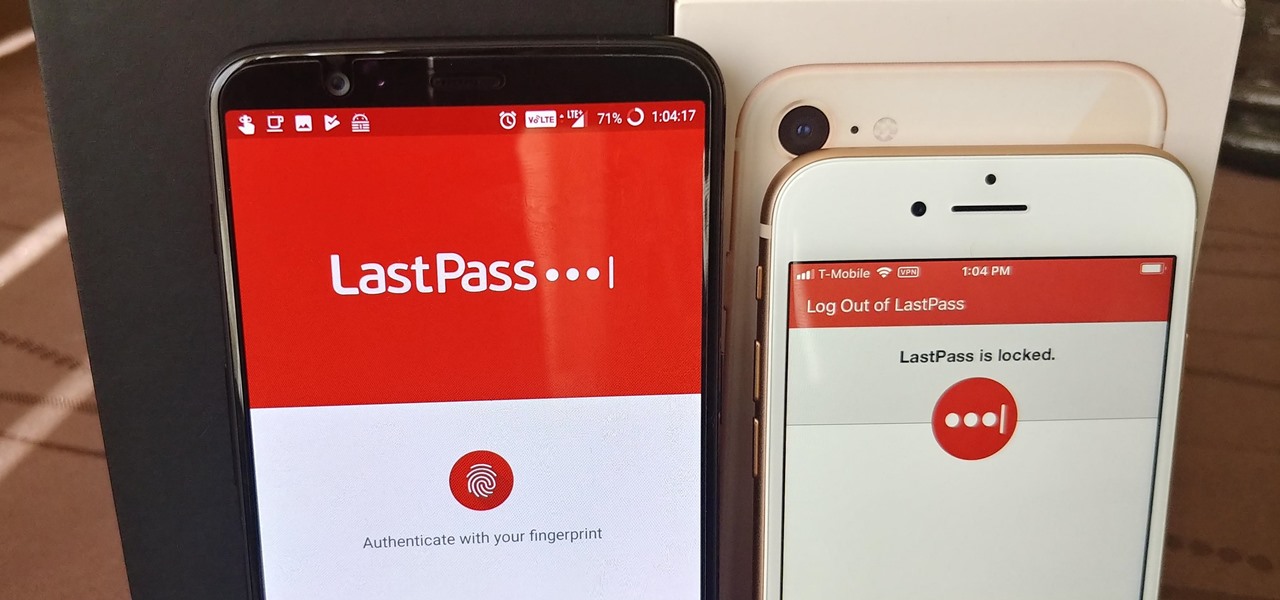
When traversing the web, you'll regularly come across websites that require you to create an account. With the majority of these accounts, protection is limited to a simple password. Despite this, many people are still using weak passwords such "123456." For these reasons, you really need a password manager, and our research has shown that LastPass is still your best bet.
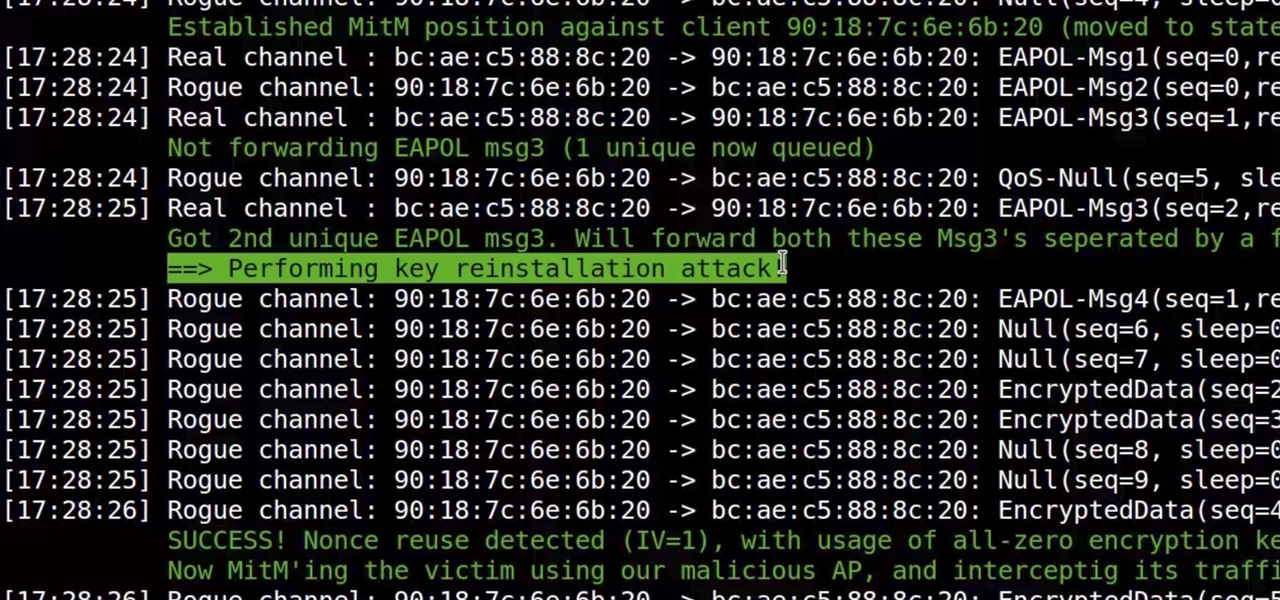
Some of us woke up at the KRACK of dawn to begin reading about the latest serious vulnerability that impacts the vast majority of users on Wi-Fi. If you weren't one of those early readers, I'm talking about the Key Reinstallation Attack, which affects nearly all Wi-Fi devices.
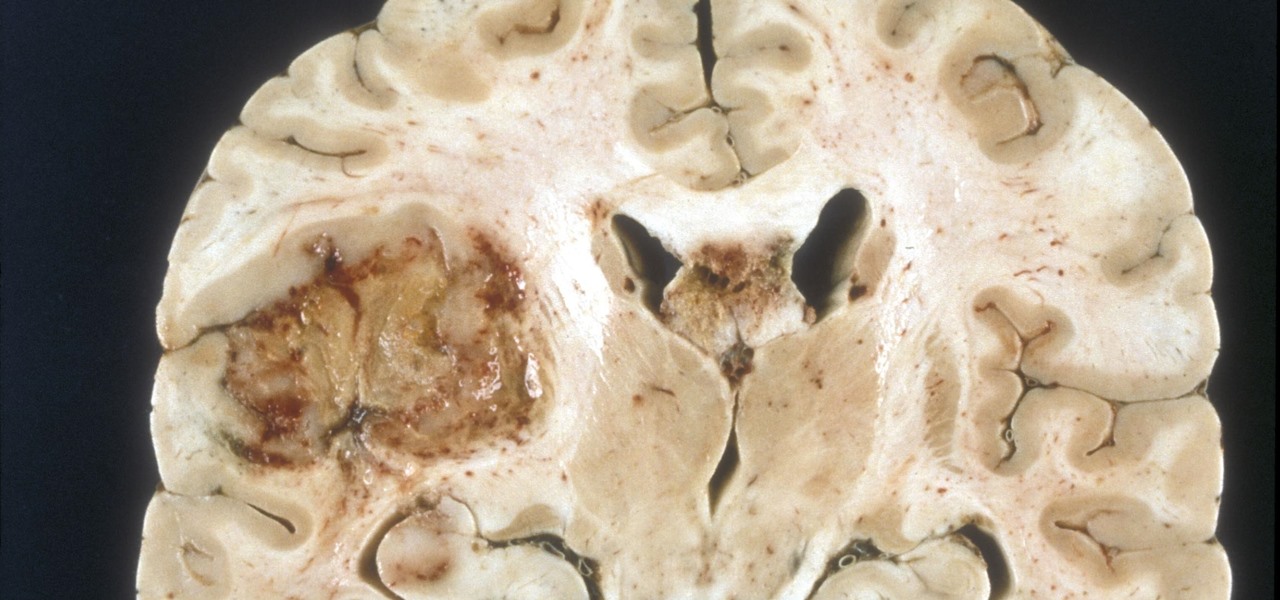
A deadly type of brain tumor and Zika-related brain damage in developing fetuses are devastating brain conditions that, at first glance, may seem unrelated. However, thanks to new research, their paths seem to cross in a way that could benefit patients. A new study has shown that Zika kills brain cancer stem cells, the kind of cells most resistant to treatment in patients with glioblastoma, a deadly brain tumor diagnosed in about 12,000 people in the US each year.
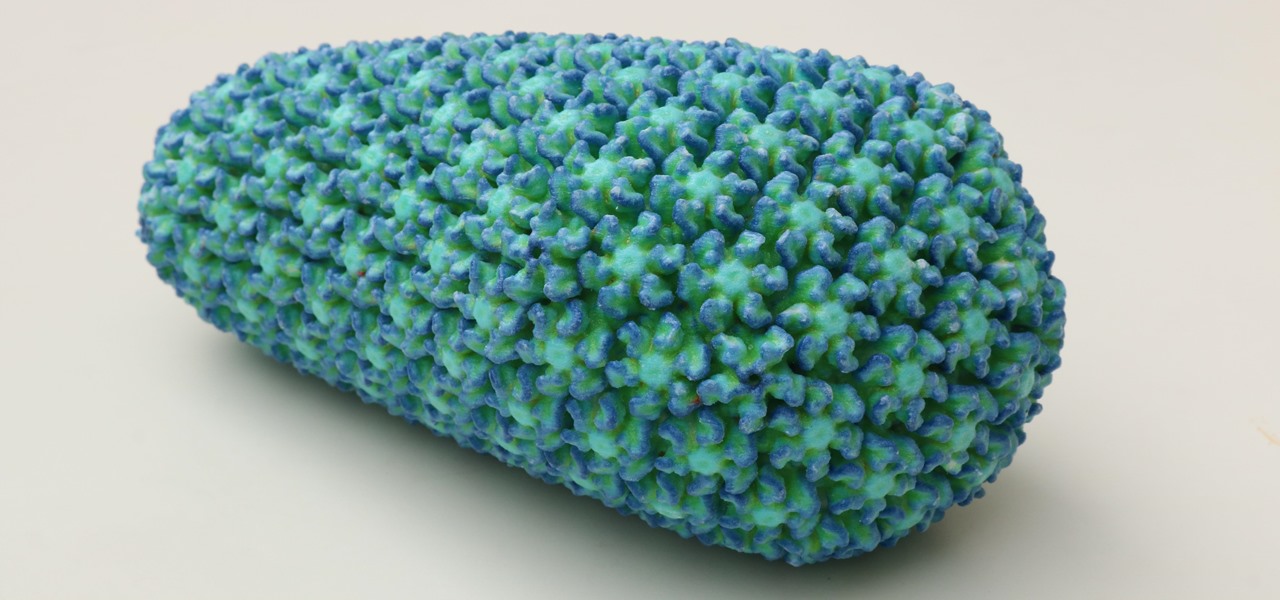
While some researchers look for drugs to treat HIV, other scientists delve deep into the virus itself for answers on how it causes infections.
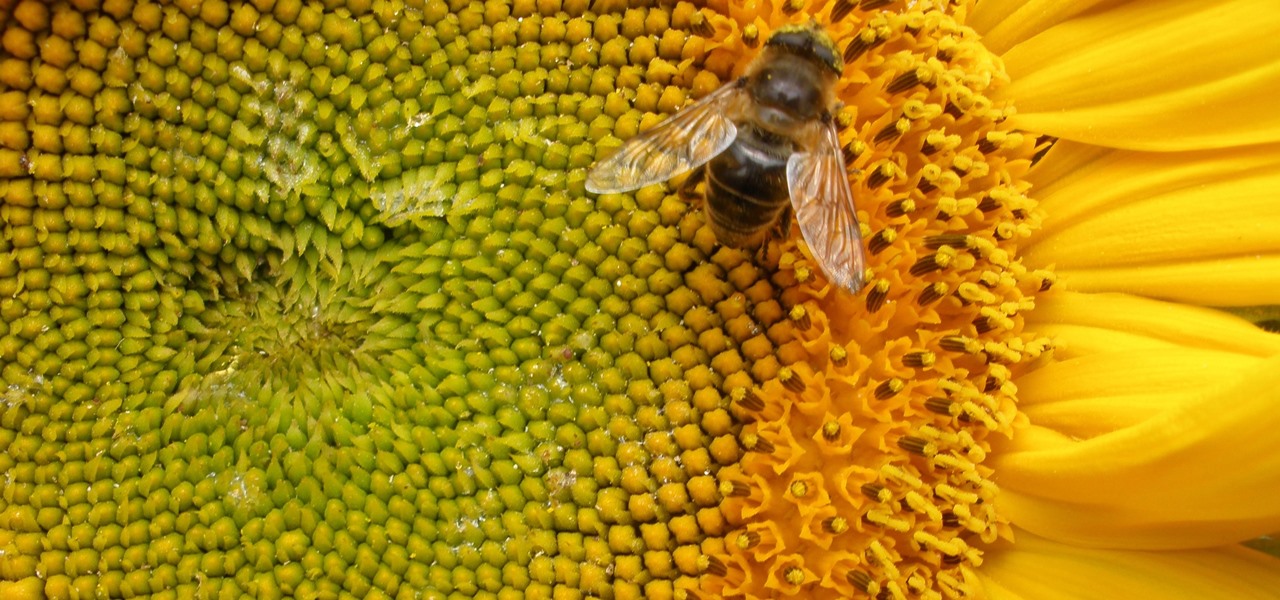

By connecting the dots between theory and real-life effect, two new studies offer more proof that neonicotinoid insecticides are causing extensive damage to honeybee colonies.
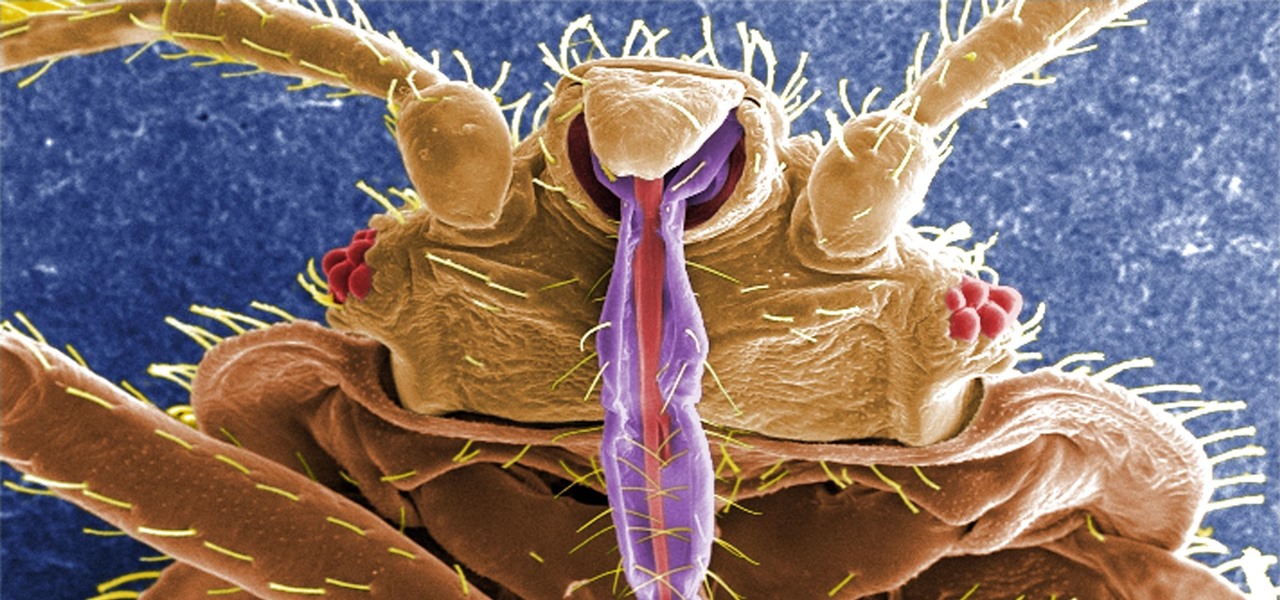
If you have encountered bed bugs lately, you are not alone. While the pesticides used to fight these pests are losing effectiveness, a fungus shows promise in knocking the bugs out of beds everywhere.
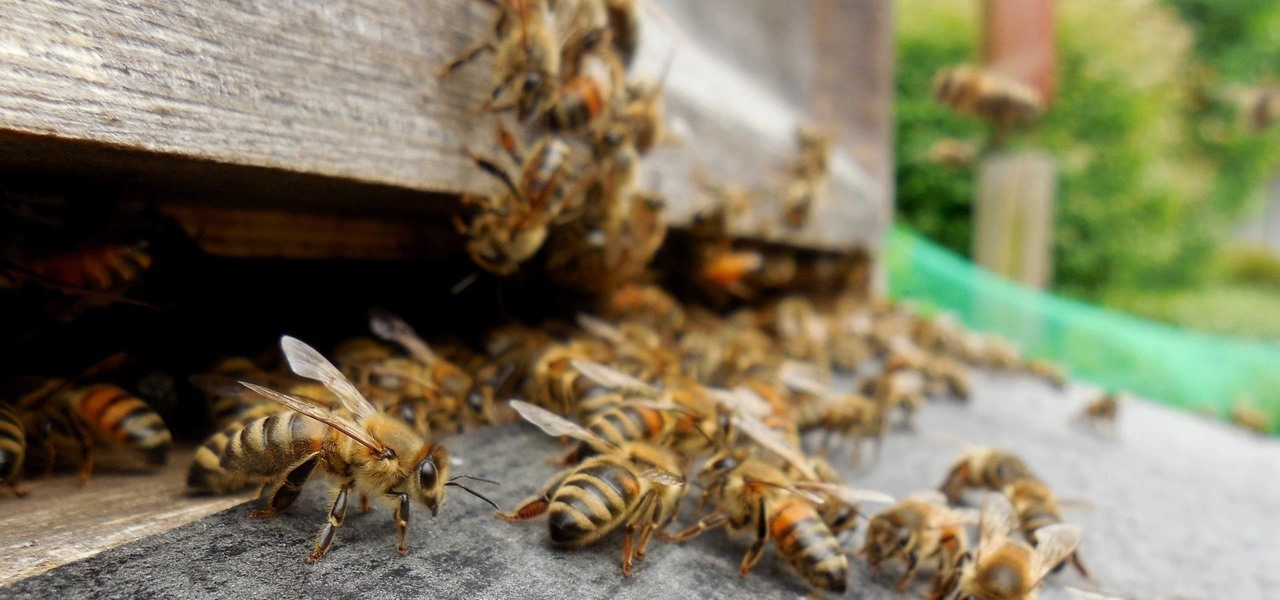

Add antibiotics to the possible list of culprits responsible for honeybee decline around the world. While it may come as a surprise, antibiotics are commonly mixed into feed used by commercial beekeepers to maintain their hives. In a recent study published in PLOS Biology, researchers from the University of Texas at Austin found antibiotics used to treat honeybees may be a contributing factor in individual bee death and colony collapse.
Six people have died from fungal infections in Pittsburgh hospitals since 2014—that fact is indisputable. The rest of the situation is much vaguer. A lawsuit has been filed against the hospitals on behalf of some of the deceased patients, alleging that moldy hospital linens are to blame. While the lawyers argue over who's at fault, let's look at how this could have happened.
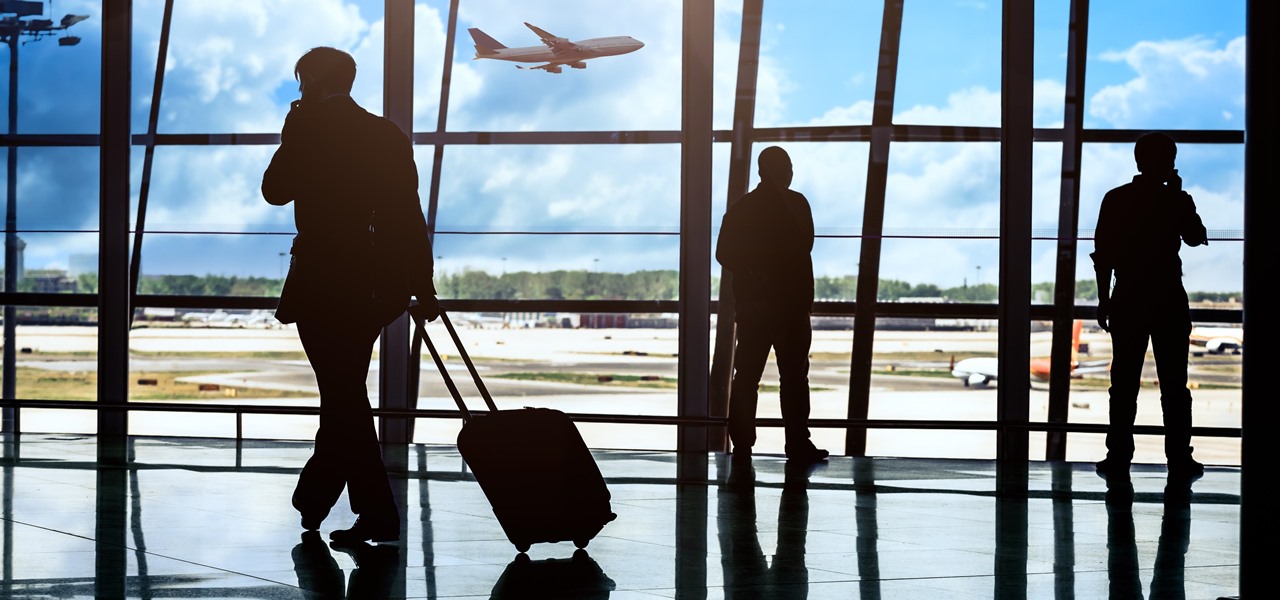

Jostled in the airport, someone is coughing in line. The air looks empty but it is loaded with microbes that make their way into your body. You get sick. You give it to your family, and that's pretty much it. But what if you were so contagious that you spread it to your entire community and beyond?
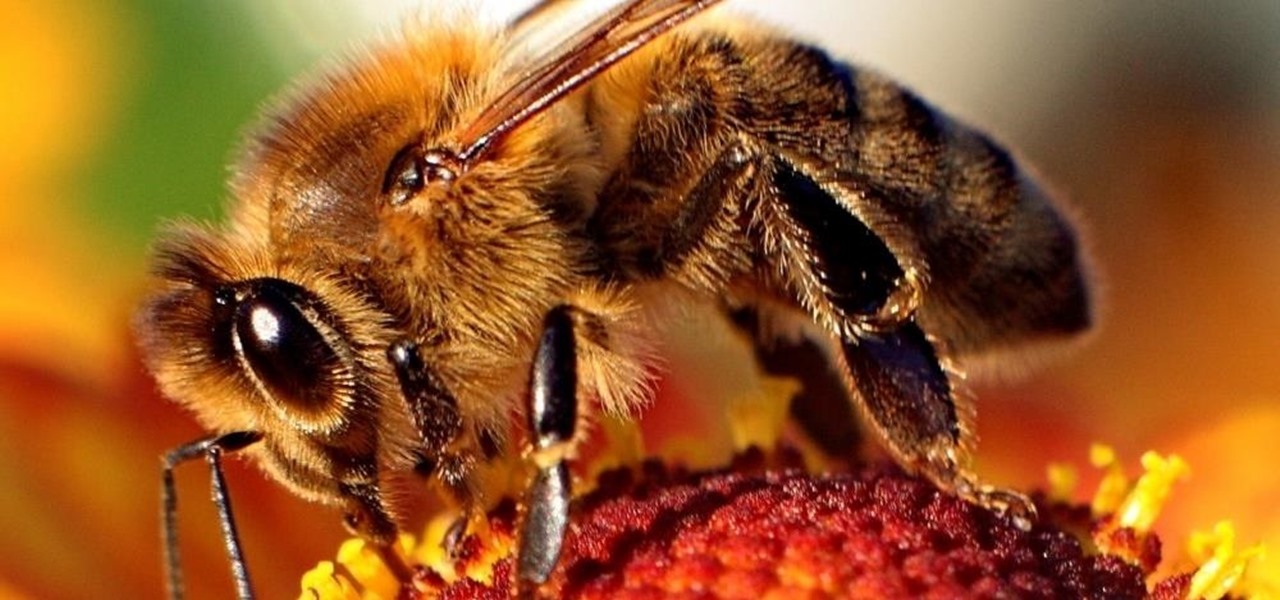

The search for the causative agent of colony collapse—the mass die off of honey bees throughout the US and Europe—has escalated with increasing confusion lately. Everything from pesticides and stress to viruses and mites have been implicated, and some researchers think that many of these environmental factors work together to take down hives.

Cats give us so much—companionship, loyalty, love... and now the bird flu. Several weeks ago, a veterinarian from the Animal Care Centers of New York City's Manhattan shelter caught H7N2 from a sick cat. According to a press release from the NYC Health Department on December 22, "The illness was mild, short-lived, and has resolved." This isn't the first time cats have passed infections on to humans, but it is the first time they passed on the bird flu—avian flu H7N2, to be exact.
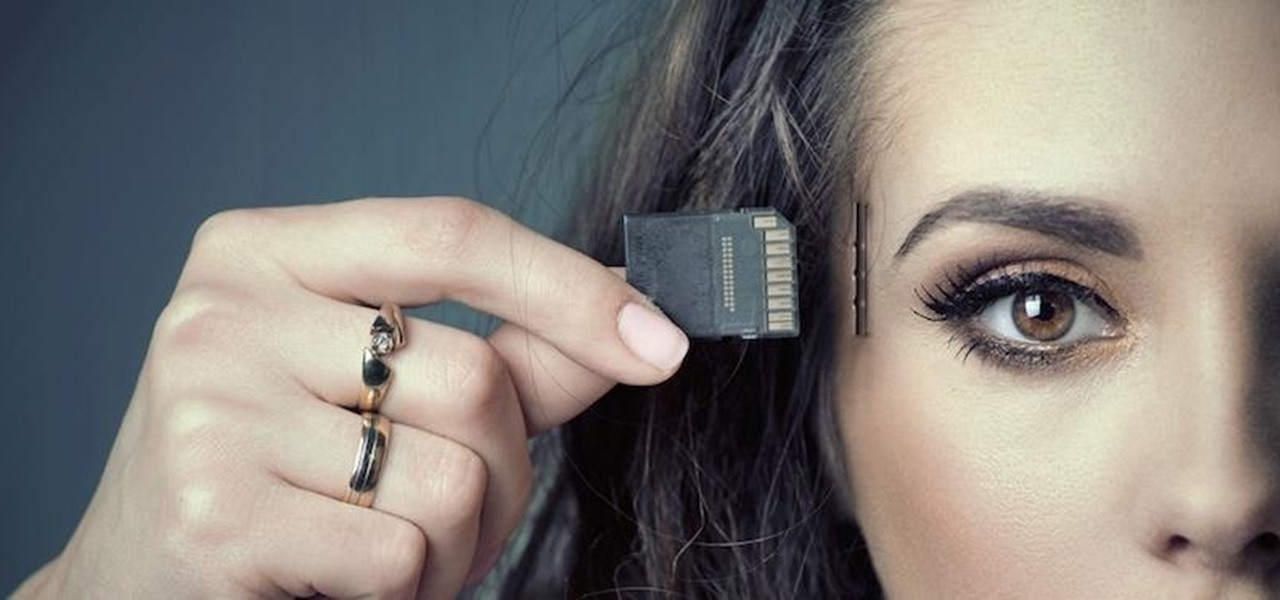

Your brain holds a lot of precious information and is capable of great feats. However, there's one quality that doesn't lie among its strengths—memory security. Yes, that's right, your brain can be hacked, and it doesn't take a psychologist to do it. Anyone with the right know-how can change your memories for their own personal benefit, and you can do so to others, too.

NOTICE: Ciuffy will be answering questions related to my articles on my behalf as I am very busy. Hope You Have Fun !!!
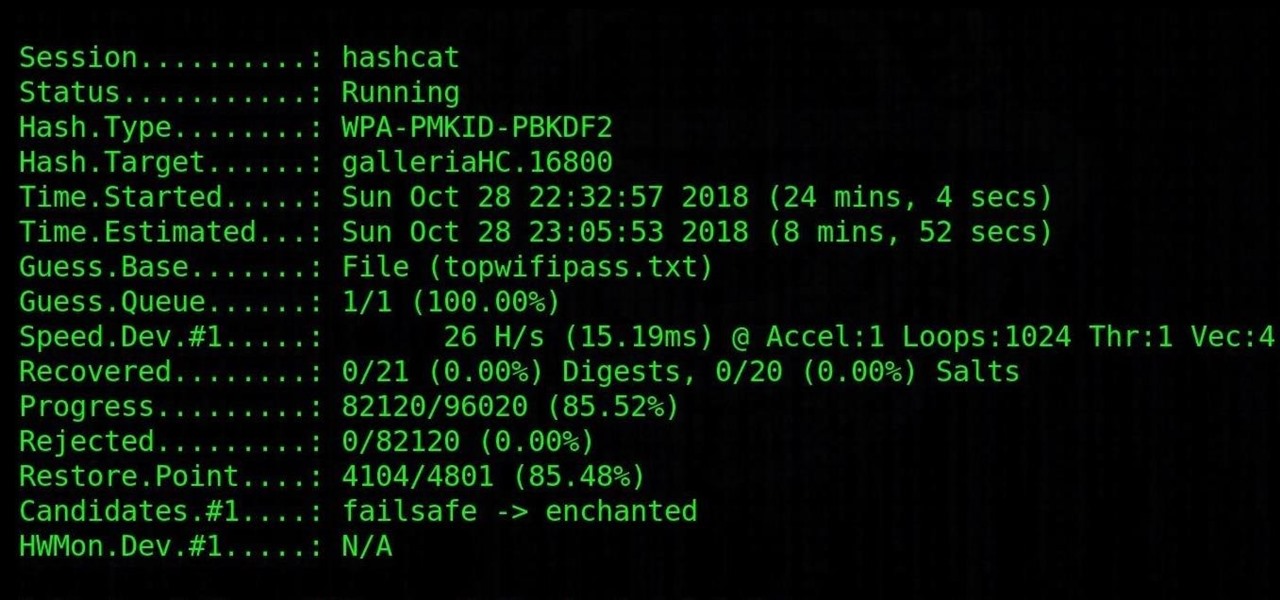
Cracking the password for WPA2 networks has been roughly the same for many years, but a newer attack requires less interaction and info than previous techniques and has the added advantage of being able to target access points with no one connected. The latest attack against the PMKID uses Hashcat to crack WPA passwords and allows hackers to find networks with weak passwords more easily.

It's not uncommon for hackers to attempt to move laterally between devices in proximity of a compromised device to maintain a prolonged presence in the network. Malware utilizing USB flash sticks to self-replicate and compromise air-gapped machines isn't a new concept.
Hashes containing login passwords are transmitted between Windows computers on local Wi-Fi networks. By intercepting and decrypting these hashes using Responder and John the Ripper, respectively, we can learn a target's login credentials which can be later used to gain physical access to their computer.
Because of the way Google Play works, Android has a "bad app" problem. Google allows any developer to upload an app to the Play Store, regardless of if it works, how it looks, or whether or not it can harm users. Malware scanning happens primarily after apps are uploaded, and though Google has recently taken steps to safeguard users with its Play Protect program, you don't have to depend on them.

If you're in the market for a new smartphone, you'll likely scan spec sheets and read reviews of the top phones, compare display size and technology, RAM amount, and processors. But one factor that is often overlooked is cell reception — and for T-Mobile subscribers, there's only one device that has flagship specs and an exclusive antenna that will actually improve your signal.
Due to the overnight success of smartphones, millions of people are connecting with others. Currently, over 15 million text messages are sent every minute worldwide. Most of this communication is happening in the open where any hacker can intercept and share in the discussion unbeknownst to the participants. However, we don't need to communicate insecurely.

After numerous scandals like the Equifax data breach and the 2016 US election, cybersecurity has become a significant issue for Americans. Unfortunately, anytime we use our devices, we're open to a cyber attack — especially when we browse the web. However, there are ways that we can make it harder for hackers and data miners.

Social engineering makes headlines because human behavior is often the weakest link of even well-defended targets. Automated social engineering tools can help reclusive hackers touch these techniques, but the study of how to hack human interactions in person is often ignored. Today, we will examine how to use subtle, hard to detect persuasion techniques to compromise a human target.